Revolutionizing Clinical Research: The Promise of Decentralized Clinical Trials
Table of Contents
Introduction
Clinical trials are the backbone of medical progress, providing essential data to bring new drugs and medical devices to market. However, the traditional model of conducting clinical trials has its limitations, often burdening participants with frequent visits to research centers and relying on paper records. In recent years, a new paradigm has emerged – Decentralized Clinical Trials (DCTs). These trials leverage technology and patient-centric approaches to transform the way we conduct research, making participation more accessible, convenient, and patient-friendly. In this blog, we’ll delve into the world of DCTs, exploring their benefits, challenges, and the potential they hold for the future of healthcare.
The Traditional Clinical Trial Landscape
Before we dive into decentralized clinical trials, it’s crucial to understand the traditional clinical trial landscape. Conventional trials involve recruiting patients who must visit research centers or hospitals for multiple assessments, treatments, and data collection points. This model has several drawbacks:
- Patient Burden: Traditional trials can be physically and emotionally demanding for participants, especially those with chronic illnesses or mobility issues. The need for frequent site visits can discourage potential participants.
- High Dropout Rates: The inconvenience and burden often lead to high dropout rates, which can compromise the integrity and completion of the study.
- Limited Diversity: Traditional trials may struggle to recruit a diverse range of participants, as access is often limited to those near research centers.
- Data Integrity: Paper-based data collection can introduce errors and delays in data analysis.
- Cost and Time-Intensive: Traditional trials are costly and time-consuming due to the need for physical infrastructure, site personnel, and extensive monitoring.
Decentralized Clinical Trials: A Paradigm Shift
Decentralized clinical trials offer a promising solution to these challenges. They leverage digital technologies and innovative methodologies to transform the clinical trial process. Here are the key features and benefits of DCTs:
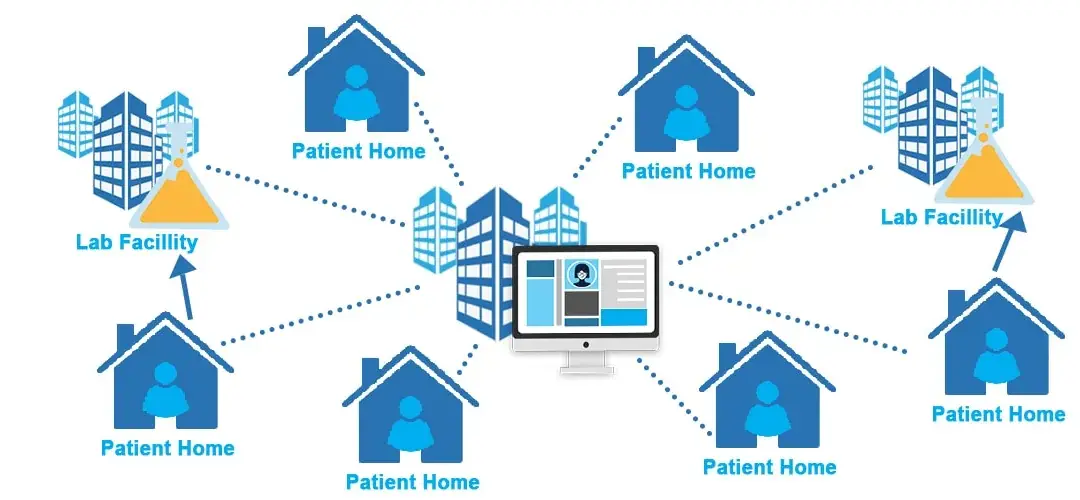
- Remote Monitoring: In DCTs, participants often use wearable devices and mobile apps to collect data related to their health and the trial parameters. This real-time data transmission allows for continuous monitoring, improving the accuracy and timeliness of data.
- Telemedicine: Virtual visits with healthcare providers or study coordinators can replace or supplement in-person visits. This not only reduces the burden on participants but also enables more frequent interactions, enhancing patient care and data collection.
- Patient-Centric Design: DCTs prioritize the patient experience, aiming to reduce the burden on participants. This patient-centered approach improves recruitment and retention rates.
- Increased Accessibility: DCTs expand access to clinical trials, allowing individuals in remote areas or with mobility limitations to participate. This inclusivity leads to more diverse and representative study populations.
- Real-World Data: DCTs can provide richer real-world data on drug efficacy and safety since they often include a broader range of participants and environments. This data is invaluable for understanding how treatments work in real-life scenarios.
- Cost Efficiency: By eliminating the need for extensive physical infrastructure and reducing site visits, DCTs can be more cost-efficient than traditional trials. This cost savings can potentially be passed on to patients and healthcare systems.
Challenges and Considerations
While DCTs hold great promise, they also face unique challenges and considerations:
- Data Security and Privacy: Ensuring the security and privacy of patient data is paramount. Robust encryption and protection measures are necessary to maintain participant trust and comply with data protection regulations.
- Regulatory Compliance: DCTs must adhere to regulatory guidelines and requirements, which can vary by country. Regulatory bodies are adapting to accommodate the unique features of decentralized trials, but navigating these regulations can be complex.
- Patient Compliance: Participants must be technologically proficient and committed to following the trial’s protocols. Ensuring patient compliance and data accuracy is essential for the success of DCTs.
- Digital Divide: DCTs may inadvertently exclude individuals without access to technology or reliable internet connectivity. Addressing the digital divide is crucial to maintaining inclusivity.
- Site Staff Adaptation: Research site staff may require additional training and support to transition from traditional to decentralized trial models effectively.
- Data Quality Assurance: Continuous remote monitoring requires robust systems for data quality assurance and real-time issue detection.
The Future of Healthcare: A DCT-Driven Revolution
Despite these challenges, decentralized clinical trials are gaining momentum and reshaping the future of healthcare and drug development. Here are some of the ways DCTs are driving this revolution:
- Faster Drug Development: DCTs accelerate the pace of drug development by streamlining data collection and analysis. This can bring life-saving treatments to patients more quickly.
- Improved Patient Engagement: By reducing the burden on participants and providing more frequent interactions with healthcare professionals, DCTs can lead to higher patient engagement and retention rates.
- Enhanced Data Quality: Real-time data collection and remote monitoring enhance the quality and reliability of clinical trial data, improving the accuracy of results.
- Greater Accessibility: DCTs make clinical trials accessible to a broader and more diverse population, leading to more inclusive research and more generalizable results.
- Reduced Costs: The cost-efficiency of DCTs can potentially lower the overall cost of healthcare and drug development, benefiting patients and healthcare systems alike.
- Personalized Medicine: DCTs can generate vast datasets that enable the development of personalized treatment approaches tailored to individual patient needs.
- Global Collaboration: DCTs facilitate international collaboration in clinical research, enabling the pooling of resources and expertise from around the world.
Conclusion
Decentralized clinical trials represent a paradigm shift in the world of clinical research. By leveraging technology and patient-centric approaches, DCTs offer a more accessible, convenient, and cost-effective model for conducting clinical trials. While they come with unique challenges, the benefits they offer in terms of data quality, patient engagement, and accelerated drug development are hard to ignore. As technology continues to advance and regulatory frameworks adapt, DCTs are poised to play a pivotal role in shaping the future of healthcare and bringing us closer to more effective treatments and cures for a wide range of diseases. The promise of DCTs lies not only in their ability to transform the clinical trial process but also in their potential to improve the overall healthcare experience for patients around the world.
You may be interested in…